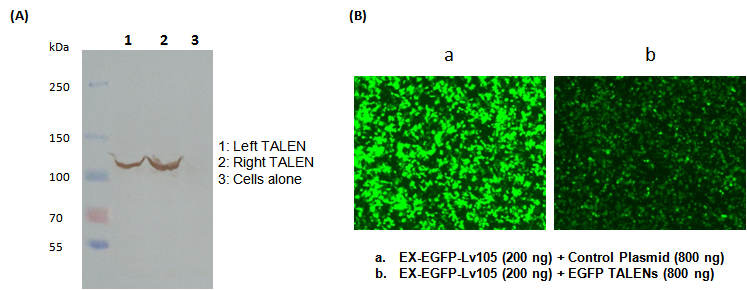
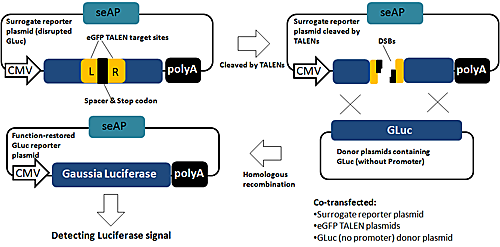
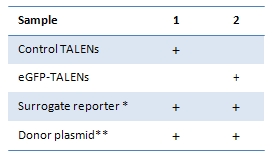
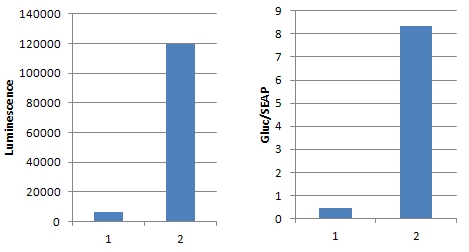
– 随心所欲基因组编辑工具 |
介绍
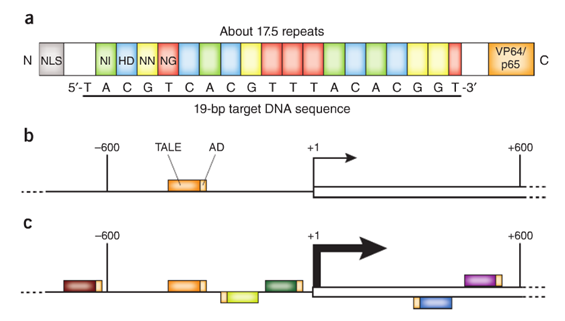
TALEs首先是在植物病原菌黄单胞菌(Xanthomonas)中发现的。当感染植物时,病原菌分泌的TALEs识别宿主植物靶基因的启动子区,调控相应基因的表达。TALE蛋白中间含有一个重复区域,该区域由33-35个氨基酸的重复单元组成。每个重复单元的氨基酸序列高度保守,除了第12位和13位的两个氨基酸可变,即重复单元可变的双氨基酸残基(RVD)。TALE单体通过RVD识别DNA靶点上的碱基,有如下一一对应关系:NI = A, HD = C, NG = T,NN = G 或 A。
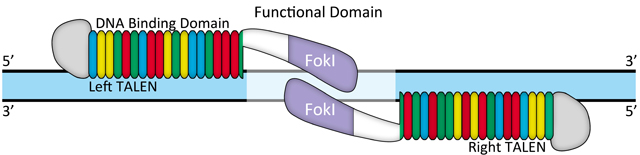
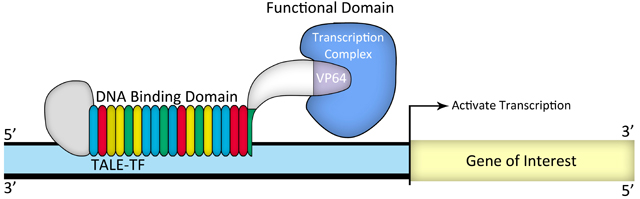
转录激活因子样效应子(TAL effectors)已广泛应用于靶向基因组操作蛋白的制备:通过融合表达核酸酶、转录因子或其他功能的结构域构建位点特异的内切酶(TALEN)、靶基因转录调控因子(TALE-TFs)或者其他基因组修饰蛋白。TALE融合蛋白通过TALE特异性识别结合染色体上靶序列进行靶向基因组编辑,比如基因敲除、基因敲入(结合使用重组供体质粒)、基因组修饰、基因转录激活或抑制等。不同于识别3联体碱基的锌指蛋白,TALE单体通过一一对应的关系精确识别单个碱基(A, T, C, G),因此可以针对基因组上任意目标序列设计组建TALE模块。
优势
- 靶向任意基因,无细胞类型限制
- 靶点在基因组上序列高度特异
- 可应用于基因敲除、基因敲入、基因修饰、基因激活或抑制等等
- 灵活的结合域和功能域设计,可选择TALEN,TALE-TF或其他TAL效应子
图 1. TALEN设计示意图
图 2. TALE-TF设计示意图
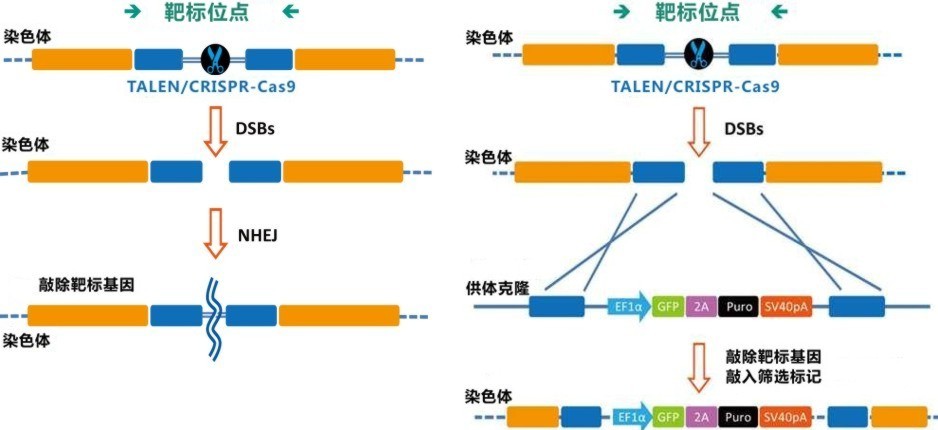
TALEN 及 CRISPR-Cas9 体系应用对比
| 性能 | TALEN | CRISPR-Cas9 |
|---|---|---|
| 识别类型 | 蛋白质-DNA | RNA-DNA |
| 甲基化敏感性 | 敏感 | 不敏感 |
| 染色质结构敏感性 | 敏感 | 敏感 |
| 脱靶效应 | 较少观察到脱靶效应 | 潜在脱靶效应高于 TALENs 及 ZFNs |
| 多靶点 | 较少使用 | 可用 |
参考文献
- Boch, J. et al. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science. 2009 326(5959):1509-12
- Moscou, M. et al. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science. 2009 326(5959):1501
- Christian, M. et al. Targeting DNA Double-Strand Breaks with TAL Effector Nucleases. DOI: 10.1534/genetics.110.120717
- Morbitzera, R. et al. Regulation of selected genome loci using de novo-engineered transcription activator-like effector (TALE)-type transcription factors. www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1013133107
- Cermak, T. et al. Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, Vol. 39, No. 12 e82 doi:10.1093/nar/gkr218
- Li, T. et al. Modularly assembled designer TAL effector nucleases for targeted gene knockout and gene replacement in eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Research, 2011, Vol. 39, No. 14 6315–6325 doi:10.1093/nar/gkr188
- Zhang, F. et al. Programmable Sequence-Specific Transcriptional Regulation of Mammalian Genome Using Designer TAL Effectors. Nat Biotechnol. 2011 February ; 29(2): 149–153. doi:10.1038/nbt.1775.